In Bacterial Communities Where Resources Are Often Limited
In communities containing Burkholderia thailandensis bacteria these abilities rely in part on contact-dependent communication with neighboring cells. As such bacteria in forest soils respond to the patchy nature of their habitat but at a scale that is difficult for us to perceive.
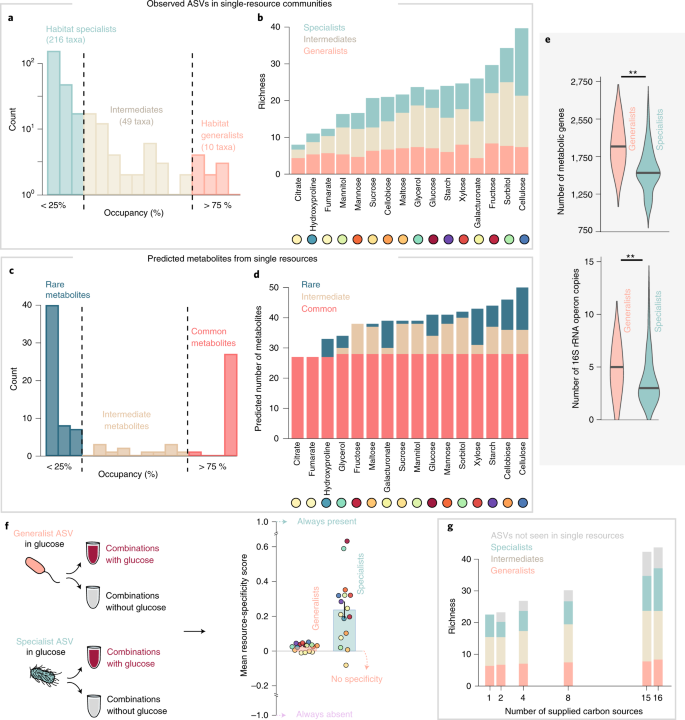
Resource Diversity Relationships In Bacterial Communities Reflect The Network Structure Of Microbial Metabolism Nature Ecology Evolution
Mechanisms of bacterial competition.
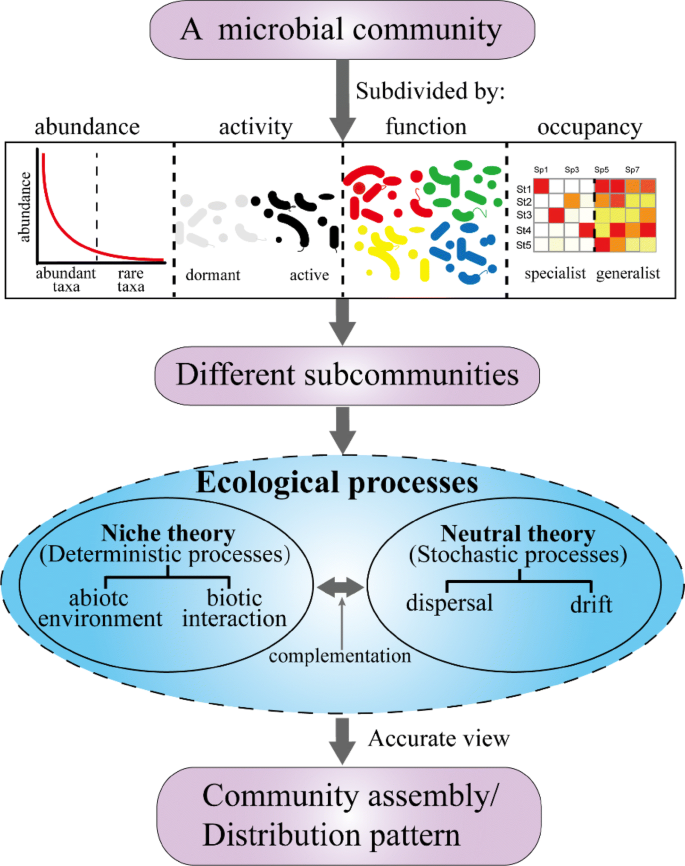
. One strategy that pathogenic bacteria use to invade the gut bacterial community is to take advantage of metabolic resources that are inaccessible to other species. The role of resources Nicholson loosely categorized competition for a limiting resource into two broad groups scramble and contest 41. In bacterial communities where resources are often limited survival requires the ability to sense respond to and cooperate or compete with neighboring organisms.
For example unlike commensal bacteria the pathogen Vibrio cholerae is able to use the abundant sialic acid found on mucins as a sole carbon source Almagro-Moreno and Boyd 2009. In communities containing Burkholderia thailandensis bacteria these abilities rely in part on contact-dependent communication with neighboring cells. Our results suggest that resource generalists can be common in aquatic bacterial communities 909192 and may explain in part why the effect of resource heterogeneity on community composition.
This communication involves a signaling protein. In bacterial communities where resources are often limited survival requires the ability to sense respond to and cooperate or compete with neighboring organisms. Within forests environmental conditions can change at very fine spatial scales.
This phenomenon is pervasive throughout the human body where commensal bacteria block the colonization of incoming microorganisms. A Describe and explain the observed results. One strategy that pathogenic bacteria use to invade the gut bacterial community is to take advantage of metabolic resources that are inaccessible to other species.
Bacteria often exist in polymicrobial communities where they compete for limited resources. Bacteria were cultured in a system that allowed for the continual addition of fresh nutrients and the removal of waste products. In communities containing Burkholderia thailandensis bacteria these abilities rely in part on contact-dependent communication with neighboring cells.
Scramble competition also called exploitation competition involves rapid utilization of the limiting resource s without direct interaction between competitors. Despite the wealth of theoretical work on how resources can affect microbial community diversity empirical tests of resourcediversity relationships have been limited having been explored. In communities containing Burkholderia thailandensis bacteria these abilities rely in part on contact-dependent communication with neighboring cells.
Intrinsic to this competition is the ability of some species to inhibit or kill their competitors. For example unlike commensal bacteria the pathogen Vibrio cholerae is able to use the abundant sialic acid found on mucins as a sole carbon source Almagro-Moreno and Boyd 2009. Fluctuations should have a great impact on bacterial communities as their duration is longer than bacterial generation times Gibson et al 2018.
In bacterial communities where resources are often limited survival requires the ability to sense respond to and cooperate or compete with neighboring organisms. Inter and intra-specific competition for food could have negative impacts on the growth and survival of smaller tadpoles. They have access to only limited resources and cannot be liberated from the changing environment.
Compared with dispersive behavior in liquid bacteria on surface environment exhibit significantly restricted mobility. Bacterial communities respond strongly to environmental drivers. As with many living organisms bacteria often live on the surface of solids such as foods organisms buildings and soil.
In bacterial communities where resources are often limited survival requires the ability to sense respond to and cooperate or compete with neighboring organisms. In bacterial communities where resources are often limited survival requires the ability to sense respond to and cooperate or compete with neighboring organisms. Such large numbers of tadpoles with limited dispersal can lead to intense competition for resources.
Bacteriophage virus were added at the time shown and the following population changes were observed. B Discuss the infection cycle of a DNA virus from attachment. Anurans are mass spawners often with multiple females spawning together resulting in thousands of tadpoles sharing a habitat.
However microcosm-experiments have shown that resource fluctuations have a low impact on bacterial communities but strong negative effects on their predators Karakoç et al 2017 2018. In communities containing Burkholderia thailandensis bacteria these abilities rely in part on contact-dependent communication with neighboring cells.
Frontiers The Origin Of Niches And Species In The Bacterial World Microbiology

How Microbes Shape Their Communities A Microbial Community Model Based On Functional Genes Sciencedirect

Synthetic Biology Tools To Engineer Microbial Communities For Biotechnology Trends In Biotechnology

Microbial Assembly Interaction Functioning Activity And Diversification A Review Derived From Community Compositional Data Springerlink
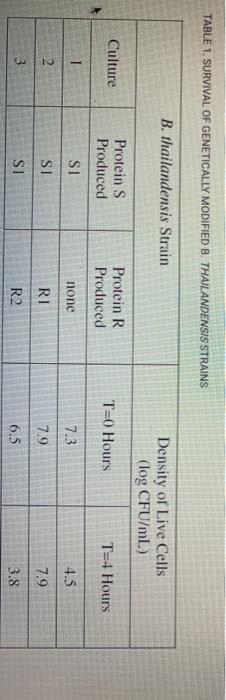
Solved Table 1 Survival Of Genetically Modified B Chegg Com
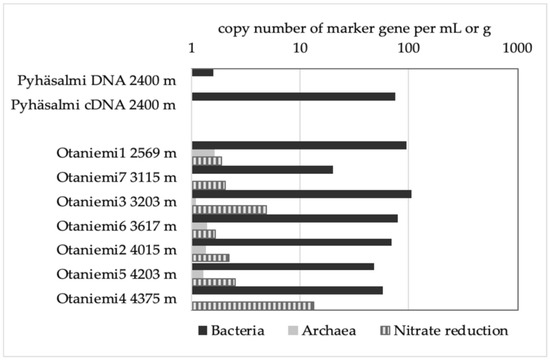
Life Free Full Text Ultradeep Microbial Communities At 4 4 Km Within Crystalline Bedrock Implications For Habitability In A Planetary Context Html
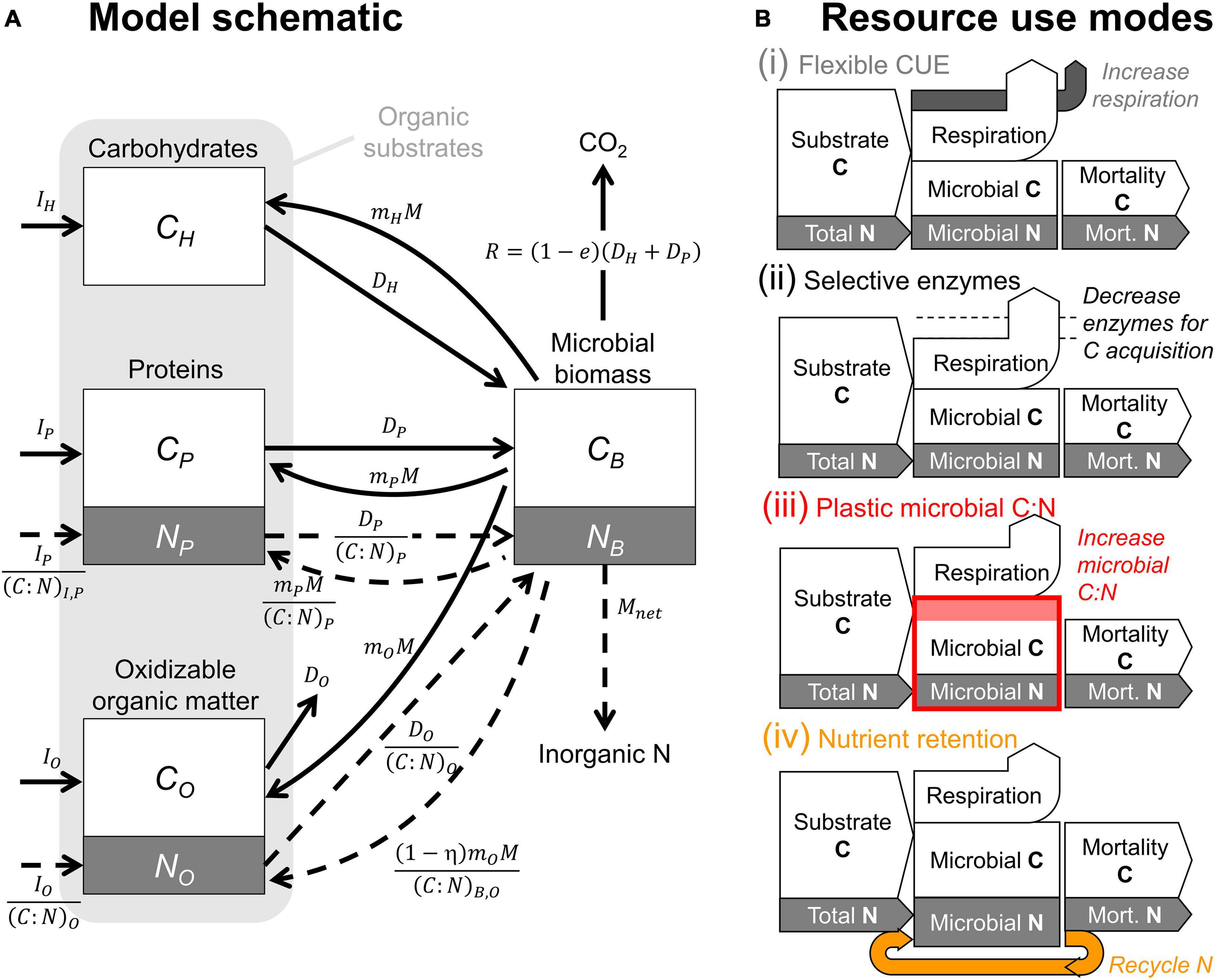
Frontiers Modeling Microbial Adaptations To Nutrient Limitation During Litter Decomposition Forests And Global Change

Top Down And Bottom Up Cohesiveness In Microbial Community Coalescence Pnas

How Microbes Shape Their Communities A Microbial Community Model Based On Functional Genes Sciencedirect
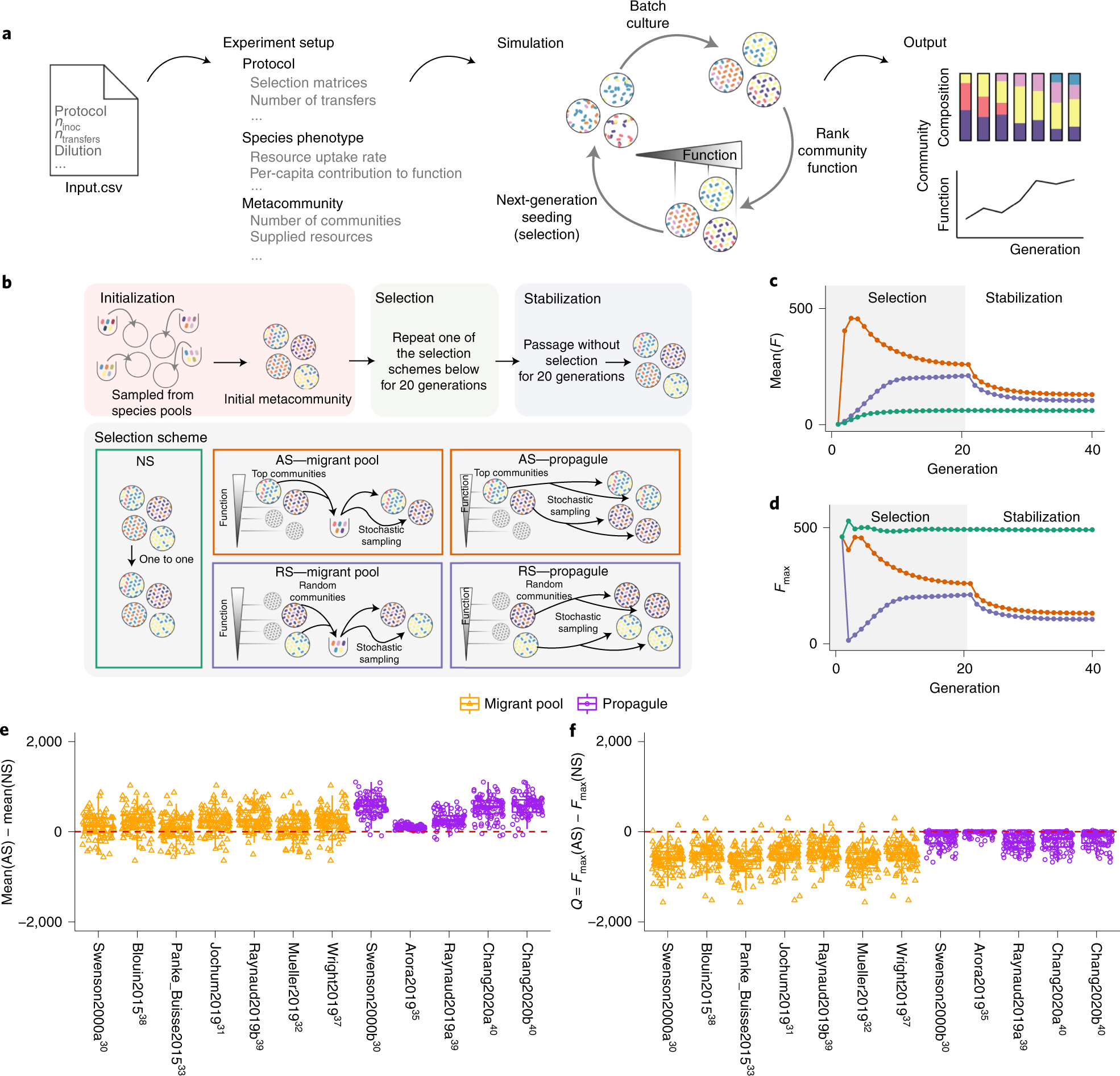
Engineering Complex Communities By Directed Evolution Nature Ecology Evolution

Michael Sims Graphing Exp Design With Se 1 3 P 1 Pdf Ap Biology 16 Pts U200bgraphing Experiment Design With Se 1 Name Michael Sims 1 In Course Hero
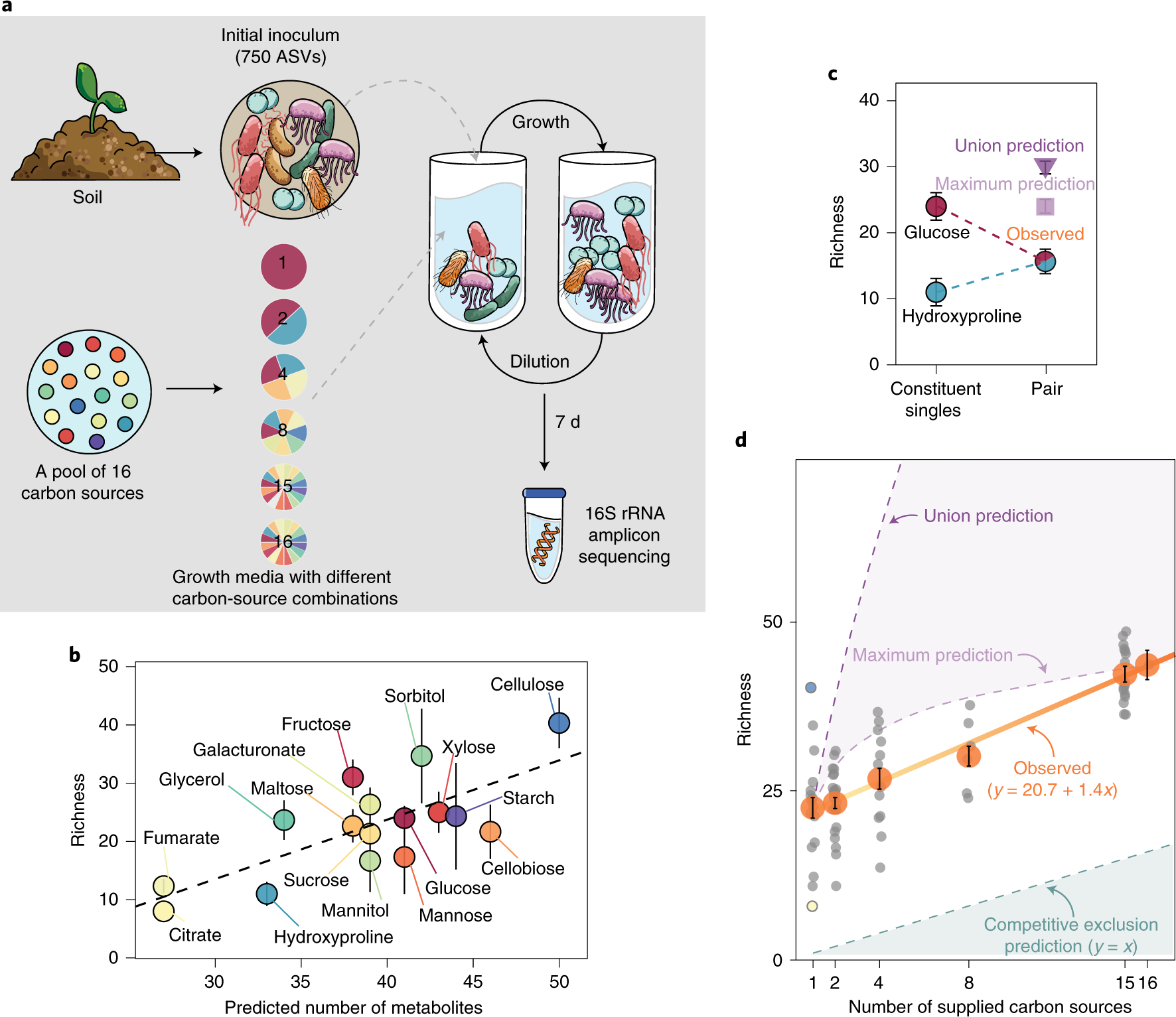
Resource Diversity Relationships In Bacterial Communities Reflect The Network Structure Of Microbial Metabolism Nature Ecology Evolution

Michael Sims Graphing Exp Design With Se 1 3 P 1 Pdf Ap Biology 16 Pts U200bgraphing Experiment Design With Se 1 Name Michael Sims 1 In Course Hero
Solved Free Response Questions 10 Points Question 2 Is A Chegg Com
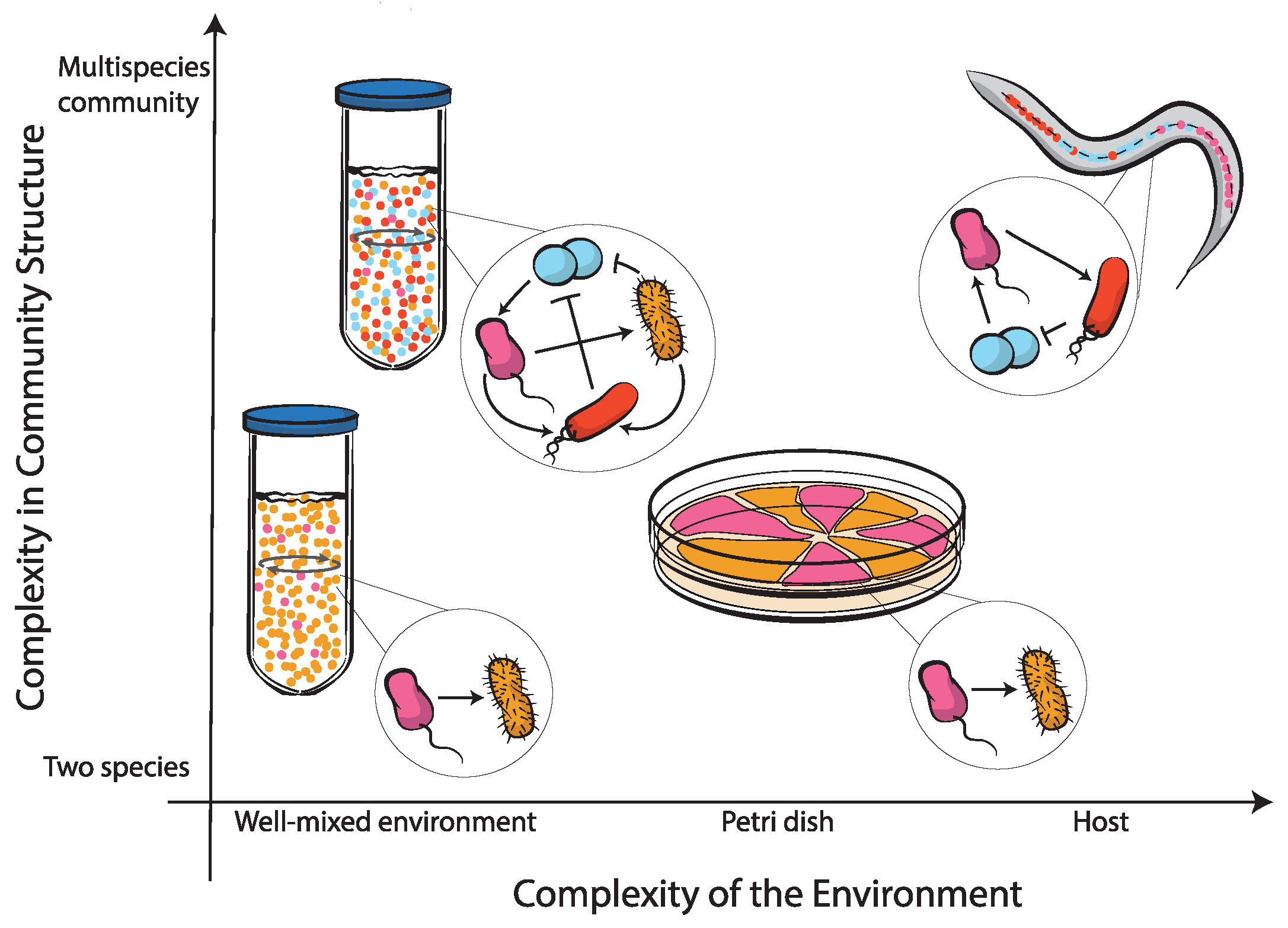
Life Free Full Text Bottom Up Approaches To Synthetic Cooperation In Microbial Communities Html

Biofilm Matrixome Extracellular Components In Structured Microbial Communities Trends In Microbiology
Solved In Bacterial Communities Where Resources Are Often Chegg Com

Deciphering The Ecology Of Cystic Fibrosis Bacterial Communities Towards Systems Level Integration Trends In Molecular Medicine
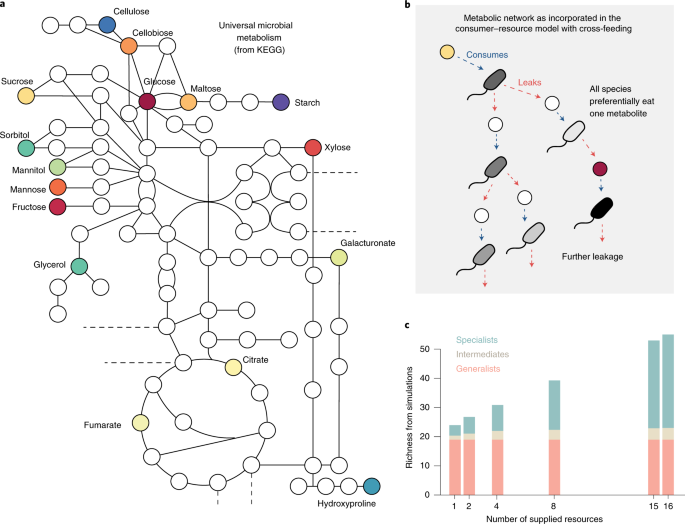
Resource Diversity Relationships In Bacterial Communities Reflect The Network Structure Of Microbial Metabolism Nature Ecology Evolution
Comments
Post a Comment